Types of Relays A Comprehensive Guide
1.Types of Relays
The core value of relays
Relays are intelligent switches in electrical systems. They play three core roles in small current, large current, and high-power circuits: isolation protection, automatic control, and signal amplification. They cover all fields including industry, automobiles, home appliances, and power.
2. The Importance of distinguishing and selecting relays
Different scenarios and different devices require the selection of corresponding relays. Choosing the wrong relay may lead to equipment damage.
Different kunds Types of Relays also come in different grades. Ordinary relays have a very short lifespan. Mechanical equipment must be equipped with relays that can maintain system stability for a long time. How to choose a relay that suits you?
3. Common relays: Electromechanical relays/solid-state relays/reed relays
1. Electromechanical relay: It is the most traditional and commonly used type on the market. It relies on electromagnetic and mechanical drives to achieve the switching of relays
Core principle: The control terminal is energized → The coil generates a magnetic field → attracts the armature (or armature) → drives the contacts to close/open → controls the load circuit. It returns to its original position by the spring after power failure.
The cost is very low, the technology is mature, and it can normally adapt to a wide range of current and voltage. However, the contacts are not anti-oxidation and are easily affected by vibration factors, resulting in poor stability
Dc electromagnetic relay: Coil wound in DC, unique contact, essential for DC equipment
Ac electromagnetic relay: Coil wound AC, built-in vibration system, essential for AC equipment
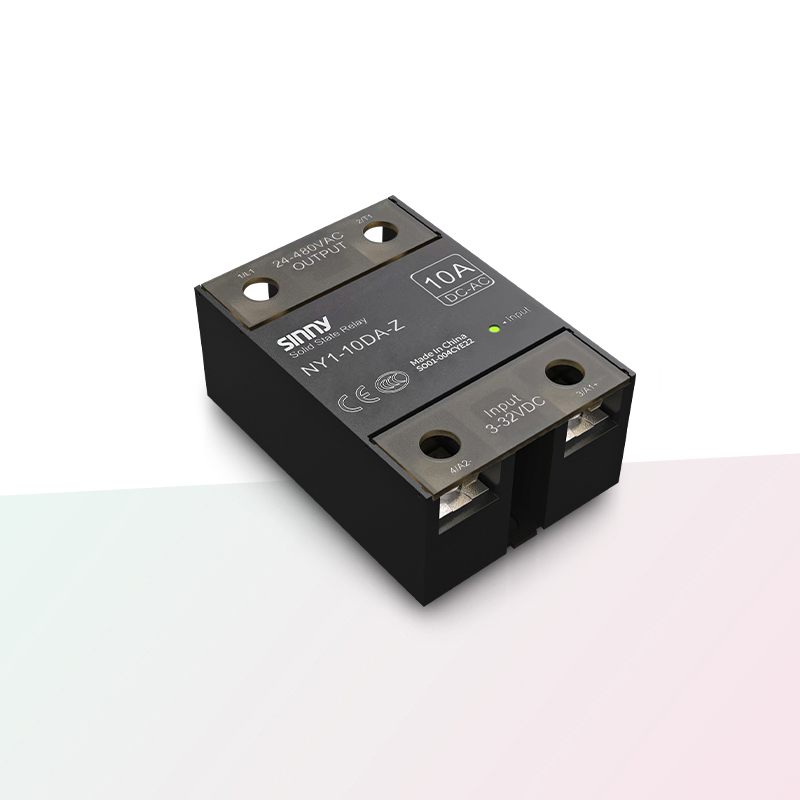

2. Solid state relay ----SSR
Switching is achieved by electronic signals, usually using semiconductor components instead of mechanical contacts, which is extremely stable
Core principle: Input signal - conduction/cut-off of semiconductor devices - achieving the on-off/turn-off of load current
As there are no moving parts, the switching speed is extremely fast, with no mechanical wear and a long service life. It also has the effects of anti-vibration and anti-corrosion, excellent heat generation and dissipation, and the wireless contacts are not explosive or flammable.
DC Solid State relay (DC-SSR) : Output control, DC load, suitable for DC motors and LED drivers
AC solid State relay (AC-SSR) : Suitable for heating systems and LED lighting control
Random SSR: Suitable for high-frequency motors and frequency converter control.
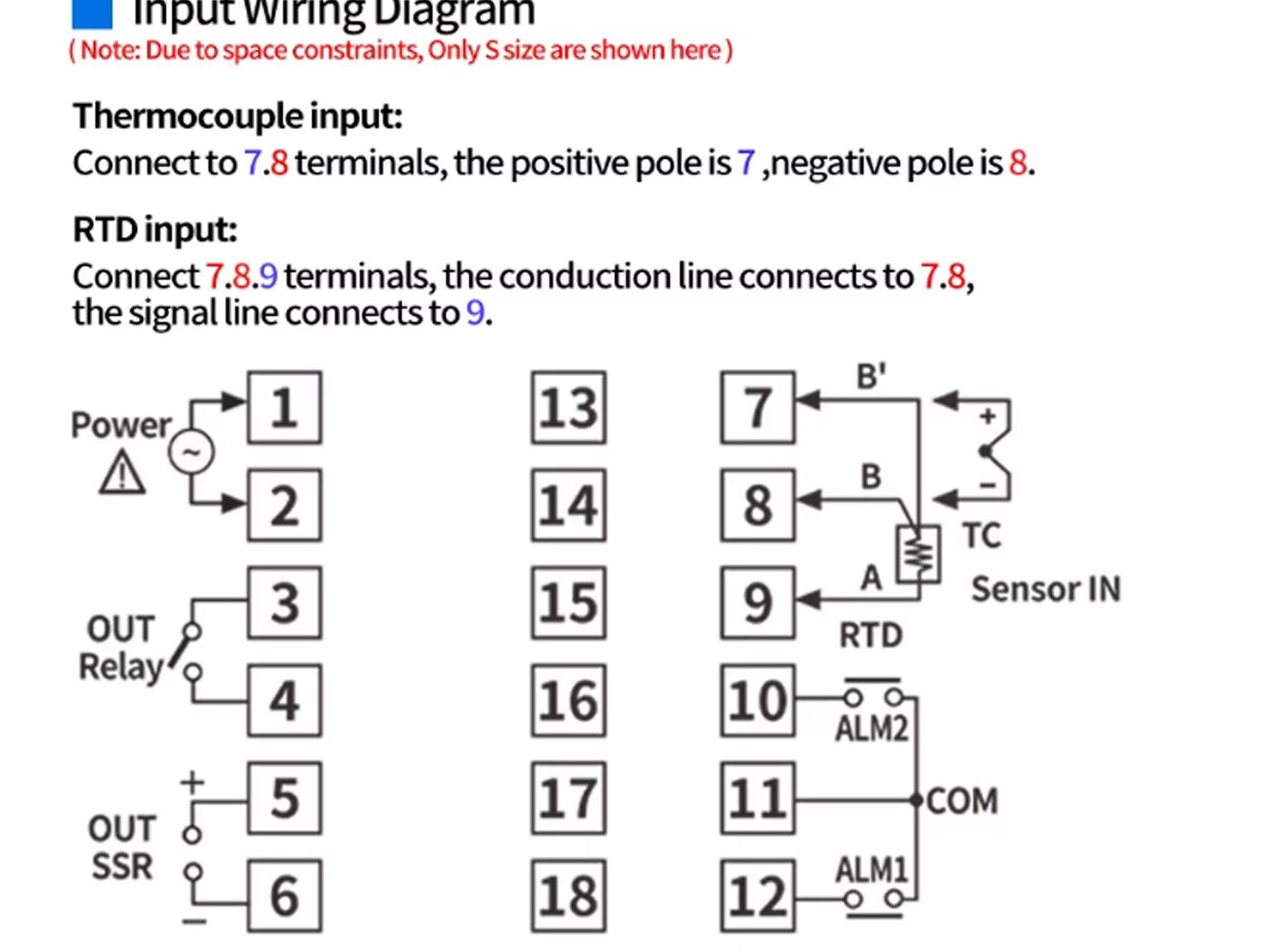
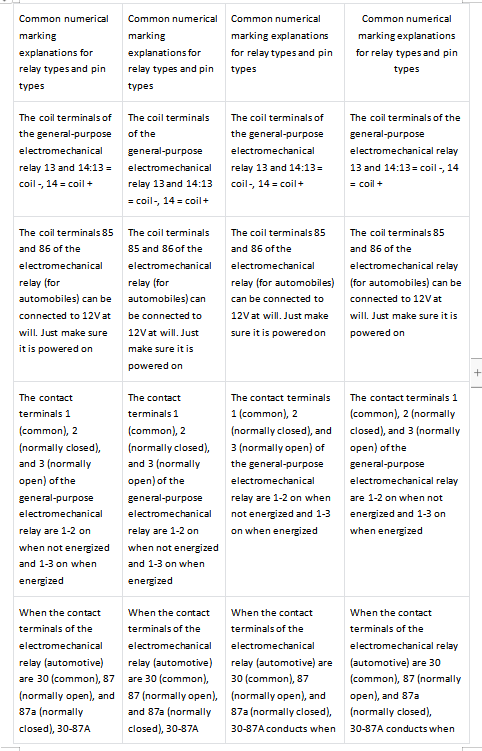
4. What do the numbers on the relay represent
Terminal: Generally marked as "13, 14" or "85, 86"
Load end: For the core, check "common end, normally open/normally closed end", and mark the numbers as "1, 2, 3" or "30, 87, 87a".
Input terminals: Generally marked with "IN+, IN-" or "1, 2"
Output terminal: Generally marked as "OUT+, OUT-" or "3, 4"
5. Relay - Function
Common relays have a timing function - timing relays/protection relays/locking relays
Principle: A delay module is added to the electromagnetic relay to set the delay duration by controlling the charging/discharging time of the capacitor.
2. Principle: Sensing data - Response - Adjustment (Protecting equipment safety)
3. When power is cut off, the original signal state is maintained. If a change is needed, the signal must be input again
6. What is the most commonly used type of contact?
When powered ON, it turns on; when powered off, it cuts off ----ON
A common terminal that can be either normally closed or normally open --CO(a combination of normally open and normally closed, pin 2)
It is on when not powered and off when powered --NC
Choose based on requirements
If you want to "work when powered on and stop when powered off" (such as turning on lights or starting motors) : Choose normally open contacts (NO), which are simple and inexpensive.
If you want to "switch between two states" (such as high and low beam, main and backup circuits) : Select the conversion contact (CO), one is equivalent to two, flexible;
Only in special scenarios such as "emergency stop and power-off to maintain operation" should normally closed contacts (NC) be selected.
Remember these two points and 99% of the scenarios won't be chosen wrongly
7. How to Choose the Right Relay - Without Getting Lost
Check the load type, DC or AC
According to the requirements, high-frequency switch/anti-vibration ---- solid state relay
Timing ----- select delay relay
The equipment to be protected ---- select the protection relay
NO (Normally Open Contact) : Open when not powered and close when powered.
- What is the principle of an analog temperature controller? Comprehensive Guide
- purpose of PID Controller - A Comprehensive Guide





















