how does a pid controller work
The PID temperature controller is a temperature regulation device based on the combination of three control algorithms: proportional, integral, and differential. It precisely calculates and outputs control signals to enable the controlled equipment to reach the desired temperature range, approach the target value, and reduce errors
Deviation (e) = Set temperature (SP) - Actualtemperature (PV)
For instance, if the set temperature is 100℃ and the actual temperature is 80℃ (with a deviation of 20℃), with Kp=0.5, then the proportional output is 10 (assuming the output range is 0-100), meaning the heater operates at 10% power. If the actual temperature drops to 50℃ (deviation of 50℃), the output increases to 25%, and the heating intensity intensifies as the deviation increases.
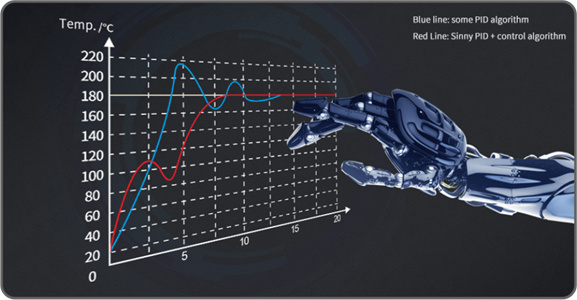
The PID temperature controller control ratio cannot eliminate the deviation ---- error

The complete working process of the PID temperature controller
Temperature collection
Deviation calculation
PID operation
Circular feedback
Monitoring and Control Ask immediately
The essence of a thermostat is a closed-loop control system. By continuously monitoring the actual temperature of the environment or equipment and comparing it with the target temperature set by the user, it automatically starts or stops heating until the temperature remains within the target range, achieving the expected effect
Generally speaking, sensors are essential elements of thermostats. Sensors are like eyes, used to receive signals. Generally, sensors are classified into bimetallic strip sensors, thermistors, thermocouples, and digital sensors
The controller is like the brain. The temperature signal obtained by the sensor will be transmitted to the controller - the brain. Heating starts when the temperature is lower than the target temperature, and cooling starts when it is higher than the target temperature, but there is a certain temperature difference of ±0.5%
Perform the adjustment
The controller's instructions are transmitted through the actuator for heating/cooling to complete temperature regulation and ultimately reach the range required for the target temperature
Regarding temperature matters
The advantages of thermostats lie in their high control accuracy, fast response speed and good stability. PID thermostats achieve precise and stable temperature regulation through the coordinated control of proportion, integration and differentiation, and are widely used in industrial manufacturing, laboratories, household appliances and other scenarios that require precise temperature control.